Cins belirleme sistemi
| |
Bu sayfanın veya bölümün Türkçeye çevrilmesi gerekmektedir. Eğer sayfanın Türkçeye çevrilmesi en fazla 2 hafta içinde gerçekleşmezse, bu sayfa veya bölüm silinme sürecine girecektir. |
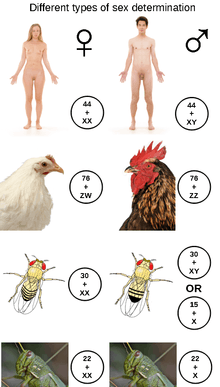
Cins belirleme sistemi, bir canlıdaki cinsel karakteristiklerin gelişimini belirleyen bir biyolojik sistem. Çoğu cinsel (eşeyli) canlı iki cinse sahiptir. Zaman zaman, bir veya her iki cins yerine hermafroditler bulunabilir. Döllenmenin olmadığı bir dişi üreme davranışı olan partenogenez sayesinde, yalnızca tek bir cinsin olduğu türler de bulunabilir.
Birçok türde, cins belirleme kalıtsaldır: Eriller ve dişiler cinsel morfolojilerini belirleyen farklı alellere ve hatta farklı genlere sahiptirler. Hayvanlarda, buna genellikle XY, ZW, XO, ZO veya haplodiploidy kombinasyonları aracılığıyla, kromozomal farklılıklar eşlik eder. Cinsel farklılaşma, genellikle bir ana gen (bir "cins lokusu") tarafından tetiklenir ve çok sayıda diğer genler de domino etkisinde bunu izler.
Diğer durumlarda, cins çevresel değişkenler (sıcaklık gibi) veya toplumsal değişkenler (örneğin, bir canlının popülasyonunun diğer üyelerine oranla boyutları) tarafından belirlenir. Çevresel cins belirlemesi kuşlar ve memelilerin kalıtsal belirlenen sistemlerinden önce gelir; bir sıcaklığa bağlı amniyotanın cins kromozomlarına sahip amniyotaların ortak atası olduğu düşünülür.
Some species do not have a fixed sex, and instead change sex based on certain cues. Bazı cins belirleme sistemlerinin ayrıntıları henüz tamamen anlaşılmış değildir.
Kromozomal belirleme
XX/XY cins kromozomları
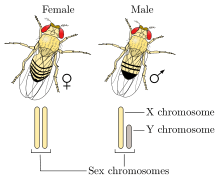
XX/XY cins belirleme sistemi, insanlarda da bulunduğu gibi, en bilinenidir. Bu sistemde, dişiler aynı çeşit cins kromozomundan (XX) iki tane bulundururken, eriller ise iki ayrı cins kromozomu (XY) bulundurur. XY cins kromozomları, otozomlardan farklı olarak şekil ve boyut açısından birbirlerinden farklıdır ve allozomlar olarak adlandırılırlar. Bazı türler (insanlar dahil) erilliği belirleyen Y kromozomunun üzerinde bir SRY genine sahipken; diğerleri ise ([[Drosofil melanogaster| Some species (including humans) have a gene SRY on the Y chromosome that determines maleness; others (such as the fruit fly) use the presence of two X chromosomes to determine femaleness.[1] Because the fruit fly, as well as other species, use the number of Xs to determine sex, they are nonviable with an extra X. SRY-reliant species can have conditions such as XXY and still live.[2] Human sex is determined by containing SRY or not. Once SRY is activated, cells create testosterone and anti-müllerian hormone to turn the genderless sex organs into male.[2] With females, their cells excrete estrogen, driving the body down the female pathway. Not all organisms remain gender indifferent for a time after they're created; for example, fruit flies differentiate into specific sexes as soon as the egg is fertilized.[2] In Y-centered sex determination, the SRY gene is not the only gene to have an influence on sex. Despite the fact that SRY seems to be the main gene in determining male characteristics, it requires the action of multiple genes to develop testes. In XY mice, lack of the gene DAX1 on the X chromosome results in sterility, but in humans it causes adrenal hypoplasia congenita.[3] However, when an extra DAX1 gene is placed on the X, the result is a female, despite the existence of SRY.[4] Also, even when there are normal sex chromosomes in XX females, duplication or expression of SOX9 causes testes to develop.[5][6] Gradual sex reversal in developed mice can also occur when the gene FOXL2 is removed from females.[7] Even though the gene DMRT1 is used by birds as their sex locus, species who have XY chromosomes also rely upon DMRT1, contained on chromosome 9, for sexual differentiation at some point in their formation.[2]
The XX/XY system is also found in most other mammals, as well as some insects. Some fish also have variants of this, as well as the regular system. For example, while it has an XY format, Xiphophorus nezahualcoyotl and X. milleri also have a second Y chromosome, known as Y', that creates XY' females and YY' males.[8] At least one monotreme, the platypus, presents a particular sex determination scheme that in some ways resembles that of the ZW sex chromosomes of birds, and also lacks the SRY gene, whereas some rodents, such as several Arvicolinae (voles and lemmings), are also noted for their unusual sex determination systems. The platypus has ten sex chromosomes; males have an XYXYXYXYXY pattern while females have ten X chromosomes. Although it is an XY system, the platypus' sex chromosomes share no homologues with eutherian sex chromosomes.[9] Instead, homologues with eutherian sex chromosomes lie on the platypus chromosome 6, which means that the eutherian sex chromosomes were autosomes at the time that the monotremes diverged from the therian mammals (marsupials and eutherian mammals). However, homologues to the avian DMRT1 gene on platypus sex chromosomes X3 and X5 suggest that it is possible the sex-determining gene for the platypus is the same one that is involved in bird sex-determination. More research must be conducted in order to determine the exact sex determining gene of the platypus.[10]
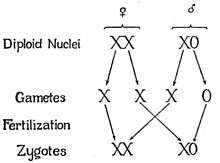
XX/X0 sex determination
In this variant of the XY system, females have two copies of the sex chromosome (XX) but males have only one (X0). The 0 denotes the absence of a second sex chromosome. Generally in this method, the sex is determined by amount of genes expressed across the two chromosomes. This system is observed in a number of insects, including the grasshoppers and crickets of order Orthoptera and in cockroaches (order Blattodea). A small number of mammals also lack a Y chromosome. These include the Amami spiny rat (Tokudaia osimensis) and the Tokunoshima spiny rat (Tokudaia tokunoshimensis) and Sorex araneus, a shrew species. Transcaucasian mole voles (Ellobius lutescens) also have a form of XO determination, in which both genders lack a second sex chromosome.[4] The mechanism of sex determination is not yet understood.[11]
The nematode C. elegans is male with one sex chromosome (X0); with a pair of chromosomes (XX) it is a hermaphrodite.[12] Its main sex gene is XOL, which encodes XOL-1 and also controls the expression of the genes TRA-2 and HER-1. These genes reduce male gene activation and increase it, respectively.[13]
ZW sex chromosomes
The ZW sex-determination system is found in birds, some reptiles, and some insects and other organisms. The ZW sex-determination system is reversed compared to the XY system: females have two different kinds of chromosomes (ZW), and males have two of the same kind of chromosomes (ZZ). In the chicken, this was found to be dependent on the expression of DMRT1.[14] In birds, the genes FET1 and ASW are found on the W chromosome for females, similar to how the Y chromosome contains SRY.[2] However, not all species depend upon the W for their sex. For example, there are moths and butterflies that are ZW, but some have been found female with ZO, as well as female with ZZW.[12] Also, while mammals inactivate one of their extra X chromosomes when female, it appears that in the case of Lepidoptera, the males produce double the normal amount of enzymes, due to having two Z's.[12] Because the use of ZW sex determination is varied, it is still unknown how exactly most species determine their sex.[12] However, reportedly, the silkworm Bombyx mori uses a single female-specific piRNA as the primary determiner of sex.[15] Despite the similarities between ZW and XY, the sex chromosomes do not line up correctly and evolved separately. In the case of the chicken, their Z chromosome is more similar to humans' autosome 9.[16] The chicken's Z chromosome also seems to be related to the X chromosomes of the platypus.[17] When a ZW species, such as the Komodo Dragon, reproduce parthenogenetically, usually only males are produced. This is due to the fact that the haploid eggs double their chromosomes, resulting in ZZ or WW. The ZZ become males, but the WW are not viable and are not brought to term.[18]
UV sex chromosomes
In some Bryophyte and some algae species, the gametophyte stage of the life cycle, rather than being hermaphrodite, occurs as separate male or female individuals that produce male and female gametes respectively. When meiosis occurs in the sporophyte generation of the life cycle, the sex chromosomes known as U and V assort in spores that carry either the U chromosome and give rise to female gametophytes, or the V chromosome and give rise to male gametophytes.[19]
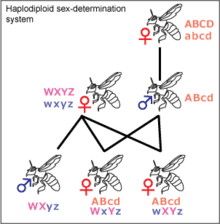
Haplodiploidy
Haplodiploidy is found in insects belonging to Hymenoptera, such as ants and bees. Unfertilized eggs develop into haploid individuals, which are the males. Diploid individuals are generally female but may be sterile males. Males cannot have sons or fathers. If a queen bee mates with one drone, her daughters share ¾ of their genes with each other, not ½ as in the XY and ZW systems. This is believed to be significant for the development of eusociality, as it increases the significance of kin selection, but it is debated.[20] Most females in the Hymenoptera order can decide the sex of their offspring by holding received sperm in their spermatheca and either releasing it into their oviduct or not. This allows them to create more workers, depending on the status of the colony.[21]
Non-genetic sex-determination systems

Temperature-dependent sex determination
Many other sex-determination systems exist. In some species of reptiles, including alligators, some turtles, and the tuatara, sex is determined by the temperature at which the egg is incubated during a temperature-sensitive period. There are no examples of temperature-dependent sex determination (TSD) in birds. Megapodes had formerly been thought to exhibit this phenomenon, but actually exhibit temperature-dependent embryo mortality.[22] For some species with TSD, sex determination is achieved by exposure to hotter temperatures resulting in the offspring being one sex and cooler temperatures resulting in the other. For others species using TSD, it is exposure to temperatures on both extremes that results in offspring of one sex, and exposure to moderate temperatures that results in offspring of the opposite sex. These systems are known as Pattern I and Pattern II, respectively. The specific temperatures required to produce each sex are known as the female-promoting temperature and the male-promoting temperature.[23] When the temperature stays near the threshold during the temperature sensitive period, the sex ratio is varied between the two sexes.[24] Some species' temperature standards are based on when a particular enzyme is created. These species that rely upon temperature for their sex determination do not have the SRY gene, but have other genes such as DAX1, DMRT1, and SOX9 that are expressed or not expressed depending on the temperature.[23] The sex of some species, such as the Nile Tilapia, Australian skink lizard, and Australian dragon lizard, is initially determined by chromosomes, but can later be changed by the temperature of incubation.[8]
It is unknown how exactly temperature-dependent sex determination evolved.[25] It could have evolved through certain sexes being more suited to certain areas that fit the temperature requirements. For example, a warmer area could be more suitable for nesting, so more females are produced to increase the amount that nest next season.[25]
Other sex-determination systems
Although temperature-dependent sex determination is relatively common, there are many other environmental systems. Some species, such as some snails, practice sex change: adults start out male, then become female (See also sex reversal). In tropical clown fish, the dominant individual in a group becomes female while the other ones are male, and bluehead wrasses (Thalassoma bifasciatum) are the reverse. In the marine worm (Bonellia viridis), larvae become males if they make physical contact with a female, and females if they end up on the bare sea floor. This is triggered by the presence of a chemical produced by the females, bonellin. Some species, however, have no sex-determination system. Hermaphrodite species include the common earthworm and certain species of snails. A few species of fish, reptiles, and insects reproduce by parthenogenesis and are female altogether. There are some reptiles, such as the boa constrictor and komodo dragon that can reproduce both sexually and asexually, depending on whether a mate is available.[26]
Other unusual systems:
- Swordtail fish[8]
- The Chironomus midge species
- The platypus has 10 sex chromosomes[9] but lacks the mammalian sex-determining gene SRY, meaning that the process of sex determination in the Platypus remains unknown.[10]
- Zebrafish go through juvenile hermaphroditism, but what triggers this is unknown.[8]
- The Platyfish has W, X, and Y chromosomes. This allows WY, WX, or XX females and YY or XY males.[8]
Evolution of sex-determination systems
Origin of sex chromosomes
The accepted hypothesis of XY and ZW sex chromosome evolution is that they evolved at the same time, in two different branches.[27][28] However, there is some evidence to suggest that there could have been transitions between ZW and XY, such as in Xiphophorus maculatus, which have both ZW and XY systems in the same population, despite the fact that ZW and XY have different gene locations.[29][30] A recent theoretical model raises the possibility of both transitions between the XY/XX and ZZ/ZW system and environmental sex determination[31] The platypus' genes also back up the possible evolutionary link between XY and ZW, because they have the DMRT1 gene possessed by birds on their X chromosomes.[32] Regardless, XY and ZW follow a similar route. All sex chromosomes started out as an original autosome of an original amniote that relied upon temperature to determine the sex of offspring. After the mammals separated, the branch further split into Lepidosauria and Archosauromorpha. These two groups both evolved the ZW system separately, as evidenced by the existence of different sex chromosomal locations.[28] In mammals, one of the autosome pair, now Y, mutated its SOX3 gene into the SRY gene, causing that chromosome to designate sex.[28][32][33] After this mutation, the SRY-containing chromosome inverted and was no longer completely homologous with its partner. The regions of the X and Y chromosomes that are still homologous to one another are known as the pseudoautosomal region.[34] Once it inverted, the Y chromosome became unable to remedy deleterious mutations, and thus degenerated.[28] There is some concern that the Y chromosome will shrink further and stop functioning in 10 million years, but other evidence has shown that the Y chromosome has been strictly conserved after its initial rapid gene loss.[35][36]
There are some species, such as the medaka fish, that evolved sex chromosomes separately; their Y chromosome never inverted and can still swap genes with the X. These species are still in an early phase of evolution with regard to their sex chromosomes. Because the Y does not have male-specific genes and can interact with the X, XY and YY females can be formed as well as XX males.[8]
Ayrıca bakınız
Şablon:Wikipedia books
- Clarence Erwin McClung who discovered the role of chromosomes in sex determination.
- Testis-determining factor
- Maternal influence on sex determination
- Protandry
- Tetrahymena have seven sexes
- İnsanlar için:
- Human sex determination and differentiation
- Eşey organı veya birincil cins özellikleri
- İkincil cins özellikleri
Kaynaklar
- ↑ Penalva, Luiz O. F.; Sánchez (September 2003). "RNA Binding Protein Sex-Lethal (Sxl) and Control of Drosophila Sex Determination and Dosage Compensation". Microbiology and Molecular Biology 67 (3): 343–359. DOI:10.1128/MMBR.67.3.343-359.2003. PMC 193869. PMID 12966139. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=193869.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Hake, Laura (2008). "Genetic Mechanisms of Sex Determination". Nature Education 1 (1). http://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/genetic-mechanisms-of-sex-determination-314. Erişim tarihi: 8 December 2011.
- ↑ Goodfellow, P. N.; Camerino, G. (1999). "DAX-1, an 'antitestis' gene". Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 55 (6–7): 857–863. DOI:10.1007/PL00013201. PMID 10412368.
- 1 2 Chandra, H. S. (25 April 1999). "Another way of looking at the enigma of sex determination in Ellobius lutescens". Current Science 76 (8): 1072.
- ↑ Cox, James J.; Willatt, L; Homfray, T; Woods, C. G. (6 January 2011). "A SOX9 Duplication and Familial 46,XX Developmental Testicular Disorder". New England Journal of Medicine 364 (1): 91–93. DOI:10.1056/NEJMc1010311. PMID 21208124.
- ↑ Huang, Bing; Wang, S; Ning, Y; Lamb, A. N.; Bartley, J (7 December 1999). "Autosomal XX sex reversal caused by duplication of SOX9". American Journal of Medical Genetics 87 (4): 349–353. DOI:10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19991203)87:4<349::AID-AJMG13>3.0.CO;2-N. PMID 10588843.
- ↑ Uhlenhaut, Henriette N.; Jakob, S; Anlag, K; Eisenberger, T; Sekido, R; Kress, J; Treier, A. C.; Klugmann, C ve diğ. (11 December 2009). "Somatic Sex Reprogramming of Adult Ovaries to Testes by FOXL2 Ablation". Cell 139 (6): 1130–1142. DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2009.11.021. PMID 20005806.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Schartl, Manfred (July 2004). "A comparative view on sex determination in medaka". Mechanisms of Development 121 (7–8): 639–645. DOI:10.1016/j.mod.2004.03.001. PMID 15210173. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925477304000371. Erişim tarihi: 6 December 2011.
- 1 2 Warren, W.C.; Hillier, Ladeana W.; Marshall Graves, Jennifer A.; Birney, Ewan; Ponting, Chris P.; Grützner, Frank; Belov, Katherine; Miller, Webb ve diğ. (2008). "Genome analysis of the platypus reveals unique signatures of evolution". Nature 453 (7192): 175–U1. Bibcode 2008Natur.453..175W. DOI:10.1038/nature06936. PMC 2803040. PMID 18464734. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2803040.
- 1 2 Gruetzner, F., T. Ashley, D. M. Rowell, and J. A. M. Graves. (2006). "Analysis of the platypus reveals unique signatures of evolution". Chromosoma 115 (2): 75–88. DOI:10.1007/s00412-005-0034-4. PMID 16344965.
- ↑ Kuroiwa A, Handa S, Nishiyama C, Chiba E, Yamada F, Abe S, Matsuda Y; Handa; Nishiyama; Chiba; Yamada; Abe; Matsuda (8 June 2011). "Additional copies of CBX2 in the genomes of males of mammals lacking SRY, the Amami spiny rat (Tokudaia osimensis) and the Tokunoshima spiny rat (Tokudaia tokunoshimensis)". Chromosome Res 19 (5): 635–44. DOI:10.1007/s10577-011-9223-6. PMID 21656076.
- 1 2 3 4 Majerus 2003
- ↑ Patricia E. Kuwabara, Peter G. Okkema, Judith Kimble; Okkema; Kimble (April 1992). [http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=275596 "tra-2 Encodes a Membrane Protein and May Mediate Cell Communication in the Caenorhabditis elegans Sex Determination Pathway"]. Molecular Biology of the Cell 3 (4): 461–73. DOI:10.1091/mbc.3.4.461. PMC 275596. PMID 1498366. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=275596.
- ↑ Smith CA, Roeszler KN, Ohnesorg T; and others; Ohnesorg; Cummins; Farlie; Doran; Sinclair (September 2009). "The avian Z-linked gene DMRT1 is required for male sex determination in the chicken". Nature 461 (7261): 267–71. Bibcode 2009Natur.461..267S. DOI:10.1038/nature08298. PMID 19710650. http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v461/n7261/full/nature08298.html.
- ↑ Kiuchi, Takashi; Koga, Hikaru; Kawamoto, Munetaka; Shoji, Keisuke; Sakai, Hiroki; Arai, Yuji; Ishihara, Genki; Kawaoka, Shinpei ve diğ. (14 May 2014). "A single female-specific piRNA is the primary determiner of sex in the silkworm". Nature 509 (7502): 633–636. Bibcode 2014Natur.509..633K. DOI:10.1038/nature13315. http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v509/n7502/abs/nature13315.html.
- ↑ Stiglec R, Ezaz T, Graves JA; Ezaz; Graves (2007). "A new look at the evolution of avian sex chromosomes". Cytogenet. Genome Res. 117 (1–4): 103–9. DOI:10.1159/000103170. PMID 17675850.
- ↑ Grützner, F.; Rens, W., Tsend-Ayush, E., El-Mogharbel, N., O'Brien, P. C. M., Jones, R. C., Ferguson-Smith, M. A. and Marshall, J. A.; Tsend-Ayush, Enkhjargal; El-Mogharbel, Nisrine; O'Brien, Patricia C. M.; Jones, Russell C.; Ferguson-Smith, Malcolm A.; Marshall Graves, Jennifer A. (2004). "In the platypus a meiotic chain of ten sex chromosomes shares genes with the bird Z and mammal X chromosomes". Nature 432 (7019): 913–917. Bibcode 2004Natur.432..913G. DOI:10.1038/nature03021. PMID 15502814.
- ↑ "Virgin births for giant lizards". BBC News. 20 December 2006. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/6196225.stm. Erişim tarihi: 13 March 2008.
- ↑ Bachtrog, D.; Kirkpatrick, M.; Mank, J.E.; McDaniel, S.F.; Pires, J.C.; Rice, W.; Valenzuela, N. (2011). "Are all sex chromosomes created equal?". Trends in genetics : TIG 27 (9): 350–357. DOI:10.1016/j.tig.2011.05.005. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0168952511000667.
- ↑ Edward O. Wilson (12 September 2005). "Kin selection as the key to altruism: its rise and fall." (PDF). Social Research 72: 1–8. http://www.thefreelibrary.com/Kin+selection+as+the+key+to+altruism%3A+its+rise+and+fall.-a0132354420. Erişim tarihi: 25 March 2011.
- ↑ Ellen van Wilgenburg; Driessen, Gerard; Beukeboom, Leow (5 January 2006). "Single locus complementary sex determination in Hymenoptera: an "unintelligent" design?". Frontiers in Zoology 3 (1): 1. DOI:10.1186/1742-9994-3-1. http://www.frontiersinzoology.com/content/3/1/1. Erişim tarihi: 22 November 2011.
- ↑ Göth, Ann; Booth, David T. (22 March 2005). "Temperature-dependent sex ratio in a bird". Biology Letters 1 (1): 31–33. DOI:10.1098/rsbl.2004.0247. PMC 1629050. PMID 17148121. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1629050.
- 1 2 Maldonado, L. C. Torres; A. Landa Piedra; N. Moreno Mendoza; A. Marmolejo Valencia (20 August 2002). "Expression profiles of Dax1, Dmrt1, and Sox9 during temperature sex determination in gonads of the sea turtle Lepidochelys olivacea". General and Comparative Endocrinology 129 (1): 20–26. DOI:10.1016/s0016-6480(02)00511-7. PMID 12409092. http://www.seaturtle.org/PDF/TorresMaldonado_2002_Ge.pdf. Erişim tarihi: 6 December 2011.
- ↑ Bull, J. J. (March 1980). "Sex Determination in Reptiles". The Quarterly Review of Biology 55 (1): 3–21. DOI:10.1086/411613. JSTOR 2826077.
- 1 2 Valenzuela, Nicole; Fredric J. Janzen (2001). "Nest-site philopatry and the evolution of temperature-dependent sex determination". Evolutionary Ecology Research 3: 779–794. http://www.public.iastate.edu/~fjanzen/pdf/01EvolEcolRes.pdf. Erişim tarihi: 7 December 2011.
- ↑ Watts, Phillip C.; Kevin R. Buley, Stephanie Sanderson, Wayne Boardman, Claudio Ciofi & Richard Gibson; Sanderson, Stephanie; Boardman, Wayne; Ciofi, Claudio; Gibson, Richard (21 December 2006). "Parthenogenesis in Komodo dragons". Nature 444 (7122): 1021–1022. Bibcode 2006Natur.444.1021W. DOI:10.1038/4441021a. PMID 17183308.
- ↑ Namekawa, Satoshi; Lee, Jeannie T. (2009). "XY and ZW: Is Meiotic Sex Chromosome Inactivation the Rule in Evolution?". PLoS Genetics (Public Library of Science) 5 (5): 3. DOI:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000493.
- 1 2 3 4 Vallender, Eric; Lahn, B. T. (28 November 2006). "Multiple independent origins of sex chromosomes in amniotes". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences) 103 (5): 18031–2. Bibcode 2006PNAS..10318031V. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0608879103. PMC 1838700. PMID 17116892. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1838700.
- ↑ Graves, Jennifer (1 September 2000). "Human Y Chromosome, Sex Determination, and Spermatogenesis—A Feminist View". Biology of Reproduction 63 (3): 667–676. DOI:10.1095/biolreprod63.3.667b (inactive 2015-02-02) . PMID 10952906.
- ↑ Ezaz, Tariq; Stiglec, Rami; Veyrunes, Frederic; Marshall Graves, Jennifer A. (5 September 2006). "Relationships between Vertebrate ZW and XY Sex Chromosome System". Current Biology 16 (16): R736. DOI:10.1016/j.cub.2006.08.021.
- ↑ Quinn, A. E.; Stephen D. Sarre; Jennifer A. Marshall Graves; Arthur Georges; Georges, A. (6 January 2011). "Evolutionary transitions between mechanisms of sex determination in vertebrates". Biology Letters 7 (3): 443. DOI:10.1098/rsbl.2010.1126. PMID 21212104. http://rsbl.royalsocietypublishing.org/content/early/2011/01/04/rsbl.2010.1126.full.pdf.
- 1 2 Graves, Jennifer (10 March 2006). "Sex Chromosome Specialization and Degeneration in Mammals". Cell 124 (5): 901–914. DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.024. PMID 16530039.
- ↑ "The evolution of the sex chromosomes: Step by step". University of Chicago Medical Center. 28 October 1999. http://www.uchospitals.edu/news/1999/19991028-x-vs-y.html. Erişim tarihi: 23 October 2011.
- ↑ Charlesworth, Brian (14 August 2003). "The organization and evolution of the human Y chromosome". Genome Biology 4 (9): 226. DOI:10.1186/gb-2003-4-9-226. PMC 193647. PMID 12952526. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=193647.
- ↑ Graves, Jennifer (22 July 2004). "The degenerate Y chromosome – can conversion save it?". Reproduction, Fertility, and Development 16 (5): 527–34. DOI:10.1071/RD03096. PMID 15367368. http://www.publish.csiro.au/?paper=RD03096.
- ↑ Hughes JF, Skaletsky H, Page DC, ""; Skaletsky; Brown; Pyntikova; Graves; Fulton; Dugan; Ding ve diğ. (22 February 2012). "Strict evolutionary conservation followed rapid gene loss on human and rhesus Y chromosomes". Nature 483 (7387): 82–86. Bibcode 2012Natur.483...82H. DOI:10.1038/nature10843. PMC 3292678. PMID 22367542. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=3292678.
Bibliyografi
- Majerus, M. E. N. (2003). Sex wars: genes, bacteria, and biased sex ratios. Princeton University Press. s. 250. ISBN 0-691-00981-3. http://books.google.com/?id=vDHOYPQ2mmYC&dq=zo,+zww,+zzww+lepidoptera. Erişim tarihi: 4 Kasim 2011.
- Beukeboom, L. & Perrin, N. (2014). The Evolution of Sex Determination. Oxford University Press. Online resources.
Şablon:Sex determination and differentiation Şablon:Chromo